Understanding and optimizing Core Web Vitals has become essential for any business looking to improve their search engine rankings and deliver exceptional user experiences. Google’s emphasis on page experience signals means that websites meeting these performance benchmarks enjoy significant advantages in search results. Whether you’re managing an e-commerce store, a corporate website, or a small business presence, mastering these metrics can dramatically transform your online success.
Key Takeaways
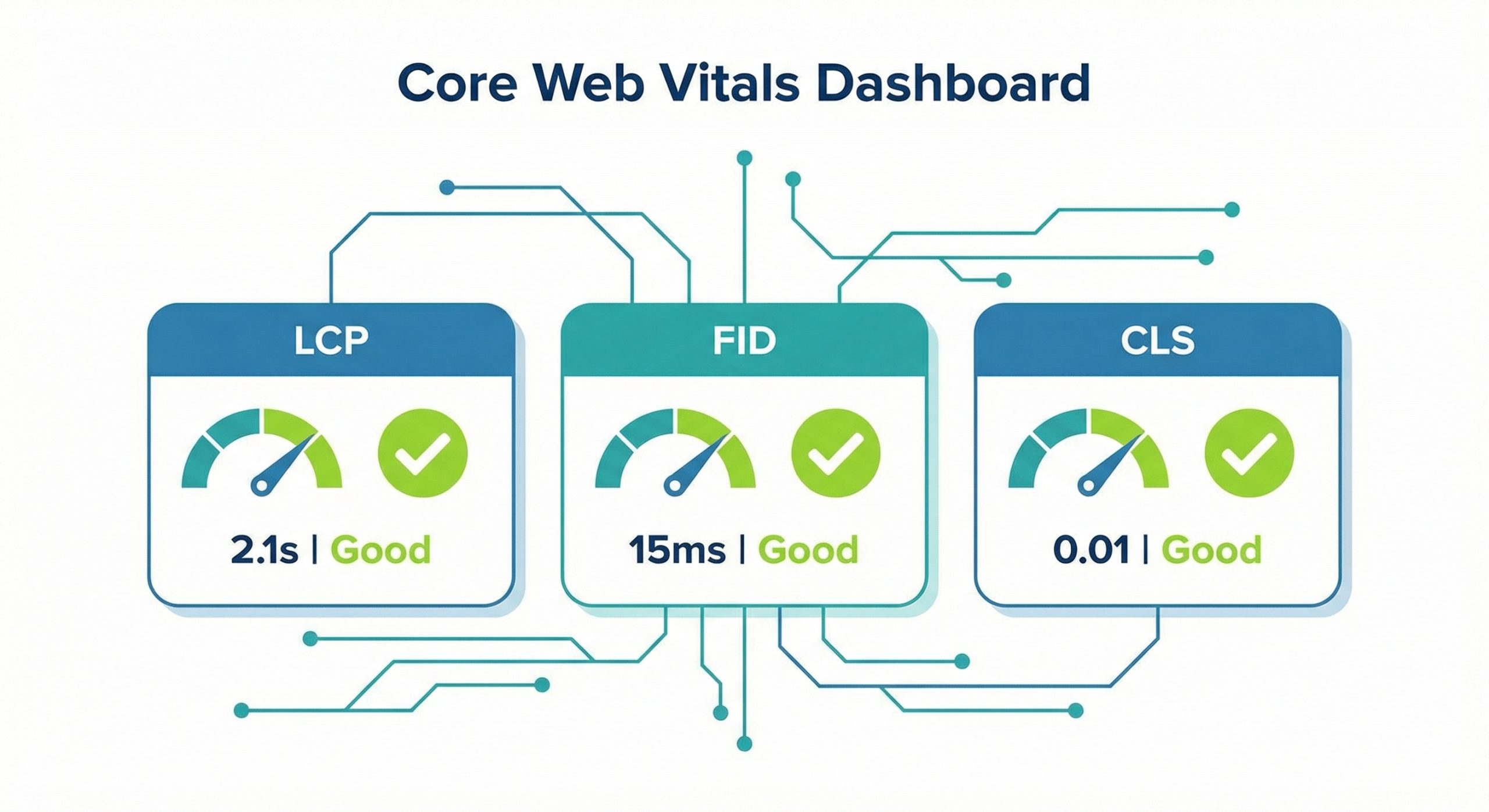
- Core Web Vitals measure real-world user experience through three key metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
- Optimizing these metrics directly impacts your search engine rankings as Google uses them as ranking factors.
- Image optimization, server response times, and JavaScript management are crucial for improving LCP scores.
- Reducing third-party script impact and minimizing main thread work improves interactivity metrics.
- Reserving space for dynamic content and using proper image dimensions prevents layout shifts.
Understanding Core Web Vitals: The Foundation of Page Experience

Core Web Vitals represent Google’s initiative to provide unified guidance for quality signals that are essential to delivering a great user experience on the web. These metrics focus on three distinct aspects of user experience: loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. By measuring these elements through real-world data, Google can better understand how users actually experience web pages.
The significance of these metrics extends beyond mere technical benchmarks. They directly correlate with user satisfaction, bounce rates, and conversion rates. Research consistently shows that websites with poor Core Web Vitals experience higher abandonment rates and lower engagement. Conversely, sites that excel in these areas see improved time on site, more page views per session, and ultimately, better business outcomes.
Largest Contentful Paint: Mastering Loading Performance
Largest Contentful Paint measures the time it takes for the largest content element visible within the viewport to become fully loaded. This could be a hero image, a large text block, or a video thumbnail. Google considers an LCP of 2.5 seconds or less as good, while anything above 4 seconds needs improvement.
Improving your LCP requires a multi-faceted approach. Start by optimizing your largest images through modern formats like WebP or AVIF, implementing lazy loading for below-the-fold content, and using responsive images with appropriate srcset attributes. Server response time plays a crucial role too, so consider upgrading your hosting infrastructure, implementing caching strategies, and utilizing Content Delivery Networks to serve assets from locations closer to your users.
Render-blocking resources often contribute to poor LCP scores. Audit your CSS and JavaScript files, defer non-critical scripts, and inline critical CSS to accelerate initial rendering. Preloading important resources using link rel=”preload” helps browsers prioritize essential content, ensuring users see meaningful content as quickly as possible.
First Input Delay and Interaction to Next Paint: Ensuring Responsiveness

First Input Delay measures the time from when a user first interacts with your page to when the browser can respond to that interaction. This metric captures how responsive your site feels during the critical first moments of user engagement. A good FID score is 100 milliseconds or less, meaning users experience virtually instantaneous feedback when they click buttons, tap links, or interact with form fields.
The primary cause of poor FID is heavy JavaScript execution. When the browser’s main thread is busy parsing, compiling, and executing JavaScript, it cannot respond to user interactions. To improve FID, break up long-running JavaScript tasks into smaller chunks, implement code splitting to load only what’s needed, and remove unused JavaScript from your bundles.
Third-party scripts often significantly impact interactivity metrics. Audit all external scripts including analytics, advertising, chat widgets, and social media embeds. Load non-essential third-party scripts asynchronously or defer them until after the main content has rendered. Consider using web workers for computationally intensive tasks to keep the main thread responsive.
Cumulative Layout Shift: Maintaining Visual Stability
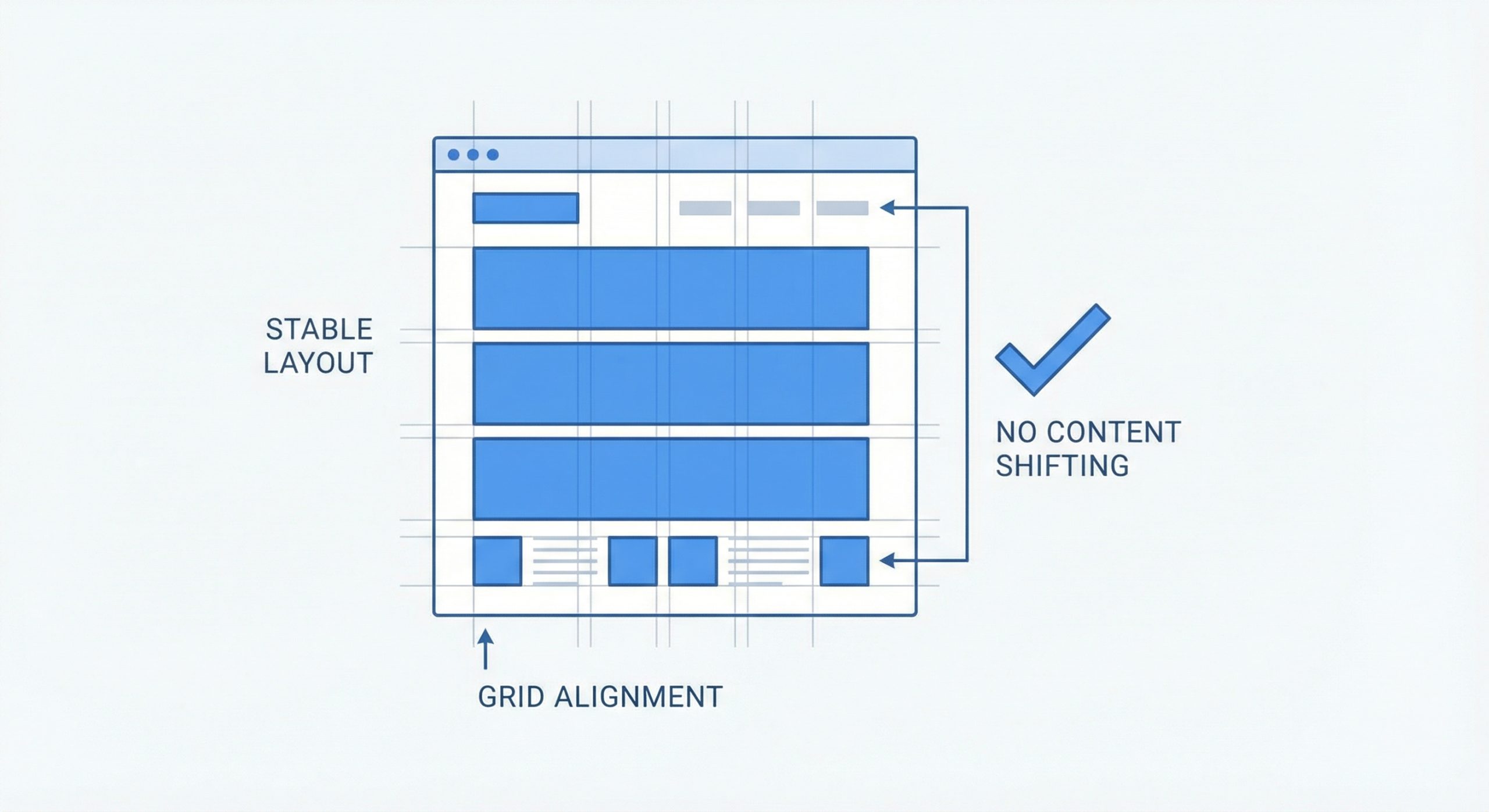
Cumulative Layout Shift measures the unexpected movement of visible content during the entire lifespan of a page. Nothing frustrates users more than reaching for a link only to have it move as an image loads above it. Google considers a CLS score of 0.1 or less as good, indicating minimal unexpected layout shifts.
Preventing layout shifts begins with always including width and height attributes on images and video elements. This allows browsers to reserve the correct amount of space before the media loads. For responsive designs, use CSS aspect ratio boxes to maintain proportions regardless of the final image dimensions.
Dynamic content injection is another common culprit. Advertisements, embedded content, and dynamically loaded sections should have reserved space in your layout. Avoid inserting content above existing content except in response to user interaction. When new content must appear, use CSS transforms or absolute positioning rather than properties that affect layout flow.
Measuring and Monitoring Your Core Web Vitals
Effective optimization requires consistent measurement. Google Search Console provides Core Web Vitals reports showing how your pages perform based on real-world data from Chrome users. PageSpeed Insights offers both lab data and field data, providing immediate feedback on potential improvements alongside actual user experience data.
Lighthouse, available in Chrome DevTools, provides detailed audits and specific recommendations for improving each metric. For more granular monitoring, the web-vitals JavaScript library can capture these metrics and send them to your analytics platform, enabling you to track performance across different user segments, devices, and pages.
Regular monitoring helps identify regressions before they impact rankings. Set up automated alerts when metrics fall below acceptable thresholds. Compare performance across page templates to identify structural issues, and test changes in staging environments before deploying to production.
The SEO Impact of Core Web Vitals Optimization
Since Core Web Vitals became an official ranking factor, websites that prioritize these metrics have seen measurable improvements in search visibility. While content relevance and traditional ranking factors remain paramount, page experience serves as a tiebreaker when multiple pages have similar content quality. In competitive markets, this distinction can mean the difference between first-page visibility and being buried in search results.
Beyond direct ranking benefits, improved Core Web Vitals contribute to better user engagement signals. Faster, more stable, and more responsive pages lead to lower bounce rates, longer session durations, and higher conversion rates. These behavioral signals further reinforce positive ranking outcomes, creating a virtuous cycle of improved performance and visibility.
Investing in Core Web Vitals optimization yields returns across multiple dimensions: better search rankings, improved user satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and stronger brand perception. As user expectations continue to rise and Google refines its algorithms, websites that excel in these foundational metrics will maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly demanding digital landscape.